Embark on a captivating journey with understanding gas laws worksheet answers, where we unveil the fundamental principles governing the behavior of gases. From Boyle’s Law to Charles’s Law and beyond, this comprehensive guide empowers you to decipher the complexities of gas dynamics and conquer worksheet challenges with confidence.
Delving into the intricacies of a typical “Understanding Gas Laws” worksheet, we explore its structure and purpose. Common problem types and exercises are identified, equipping you with the tools to navigate these worksheets effectively.
Gas Laws and Their Applications: Understanding Gas Laws Worksheet Answers
Gas laws are a set of principles that describe the behavior of gases under various conditions. These laws provide a framework for understanding and predicting the properties of gases, making them essential in fields such as chemistry, physics, and engineering.
Boyle’s Law
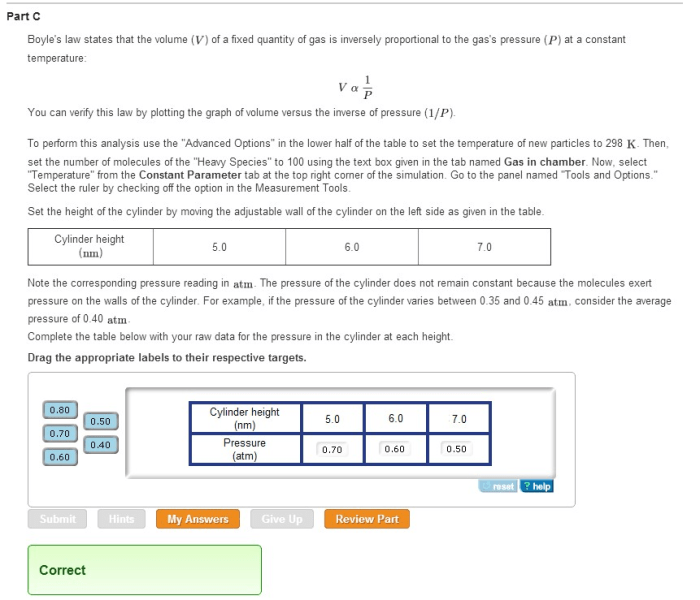
Boyle’s Law states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume at constant temperature. This means that as the volume of a gas increases, its pressure decreases, and vice versa. This relationship is often expressed mathematically as P₁V₁ = P₂V₂, where P₁ and V₁ represent the initial pressure and volume, and P₂ and V₂ represent the final pressure and volume.
Charles’s Law
Charles’s Law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature at constant pressure. This means that as the temperature of a gas increases, its volume increases, and vice versa. This relationship is often expressed mathematically as V₁/T₁ = V₂/T₂, where V₁ and T₁ represent the initial volume and temperature, and V₂ and T₂ represent the final volume and temperature.
Gay-Lussac’s Law, Understanding gas laws worksheet answers
Gay-Lussac’s Law states that the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature at constant volume. This means that as the temperature of a gas increases, its pressure increases, and vice versa. This relationship is often expressed mathematically as P₁/T₁ = P₂/T₂, where P₁ and T₁ represent the initial pressure and temperature, and P₂ and T₂ represent the final pressure and temperature.
Question Bank
What is the significance of understanding gas laws?
Understanding gas laws provides a foundation for comprehending the behavior of gases in various applications, from weather forecasting to industrial processes.
How can I effectively solve gas law problems?
Follow the step-by-step methods Artikeld in this guide, utilizing the provided formulas and tables for accurate problem-solving.
What are some common sources of error in gas law experiments?
Temperature fluctuations, measurement inaccuracies, and gas impurities can introduce errors. Understanding these sources helps minimize their impact on experimental results.
