Select all of the following that are functions of meiosis, a crucial process in sexual reproduction. Meiosis promotes genetic diversity, facilitates gamete formation, reduces chromosome number, and enables independent assortment. Understanding these functions is essential for grasping the intricacies of meiosis and its significance in biological systems.
Meiosis plays a pivotal role in ensuring genetic variation within populations, enabling adaptation to changing environments. It also contributes to the formation of gametes, the reproductive cells that combine during fertilization. Moreover, meiosis reduces the chromosome number by half, maintaining the species’ characteristic chromosome number from generation to generation.
Functions of Meiosis: Select All Of The Following That Are Functions Of Meiosis
Meiosis is a specialized form of cell division that produces gametes (sex cells) in sexually reproducing organisms. It plays a crucial role in genetic diversity, gamete formation, chromosome reduction, and independent assortment of chromosomes.
Genetic Diversity
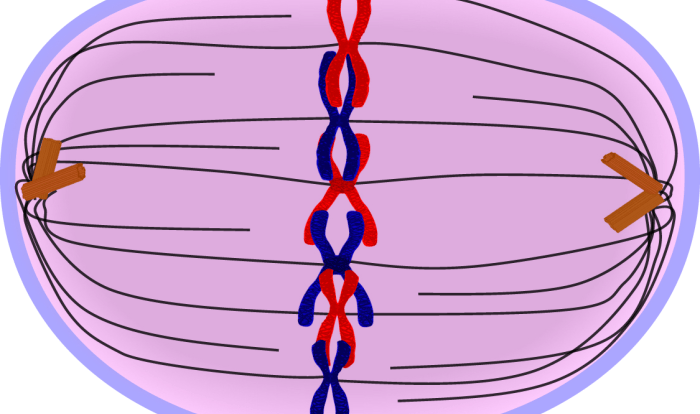
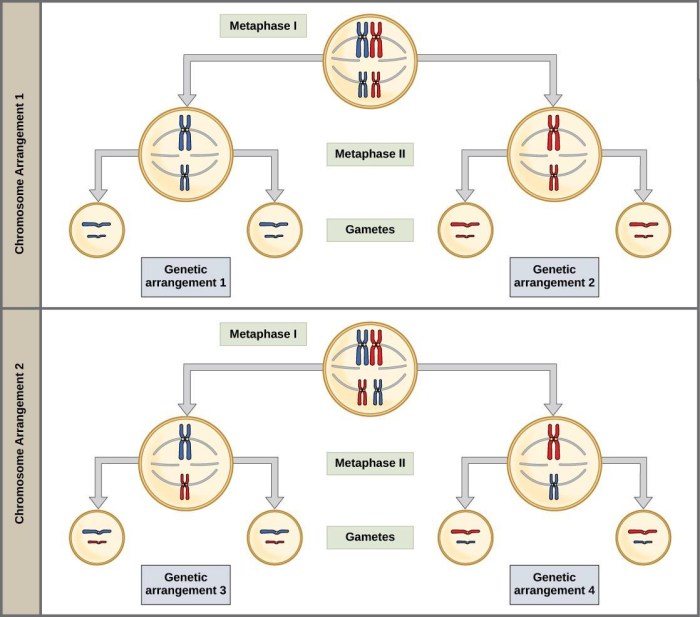
Meiosis promotes genetic diversity through the random assortment of chromosomes during cell division. During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes align randomly and exchange genetic material through a process called crossing over. This recombination event results in a unique combination of alleles on each chromosome, creating genetic diversity among gametes.
Genetic diversity is essential for the survival and adaptation of species. It allows for a wider range of traits within a population, increasing the chances of individuals possessing favorable adaptations for their environment. For example, in a population of plants, genetic diversity ensures that some individuals may have drought-tolerant traits, while others may have disease resistance or faster growth rates.
Gamete Formation, Select all of the following that are functions of meiosis
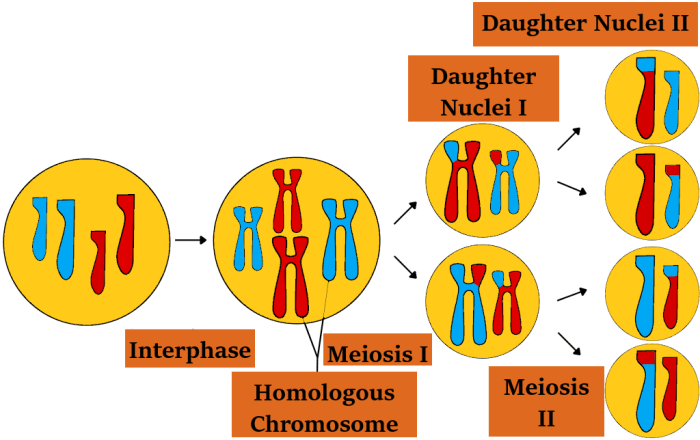
Meiosis is responsible for producing gametes (eggs and sperm) in sexually reproducing organisms. The process involves two consecutive divisions, meiosis I and meiosis II. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair up and undergo crossing over. The resulting cells then divide, reducing the chromosome number by half.
In meiosis II, the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate, resulting in four haploid gametes.
Chromosome Reduction
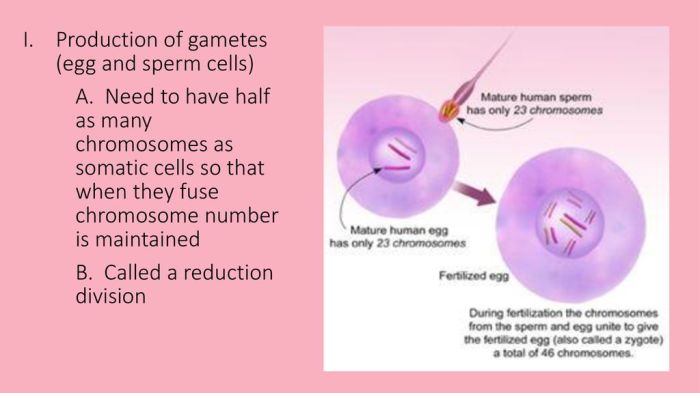
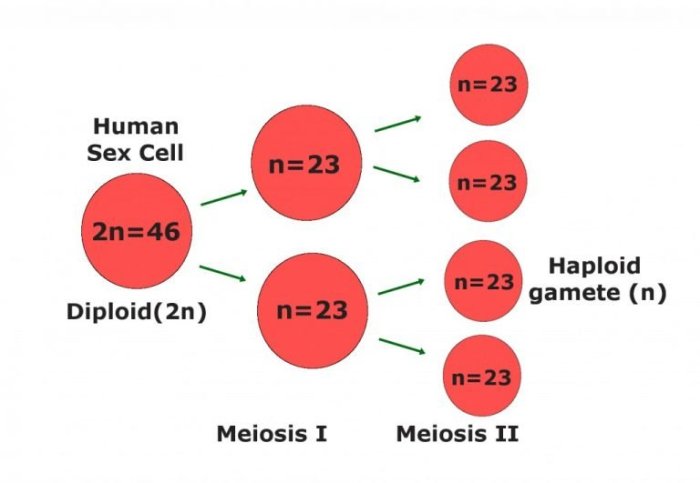
Meiosis plays a critical role in chromosome reduction. In somatic cells (body cells), the diploid number of chromosomes is maintained. However, in gametes, the chromosome number is reduced to half, creating haploid cells. This halving of chromosomes ensures that when gametes fuse during fertilization, the resulting zygote has the correct diploid number of chromosomes.
For example, in humans, somatic cells contain 46 chromosomes, while gametes (eggs and sperm) contain 23 chromosomes. When fertilization occurs, the zygote inherits 23 chromosomes from each parent, resulting in a diploid cell with 46 chromosomes.
Independent Assortment
Independent assortment is a key feature of meiosis that contributes to genetic diversity. During meiosis I, the orientation of homologous chromosomes is random. This means that the alleles on different chromosomes assort independently of one another. As a result, each gamete receives a unique combination of alleles, further increasing genetic diversity.
Independent assortment has significant implications for the inheritance of traits. For instance, if a pea plant has one allele for purple flowers and one allele for white flowers, independent assortment ensures that half of the gametes will carry the purple allele and half will carry the white allele.
When these gametes combine during fertilization, the resulting offspring will have a 50% chance of inheriting purple flowers and a 50% chance of inheriting white flowers.
Helpful Answers
What is the significance of genetic diversity in meiosis?
Genetic diversity is crucial for the survival and adaptation of species. It allows populations to possess a wide range of traits, increasing the likelihood that some individuals will have traits that are advantageous in changing environmental conditions.
How does meiosis contribute to gamete formation?
Meiosis is responsible for producing gametes, the reproductive cells that combine during fertilization. Through the processes of meiosis I and meiosis II, the number of chromosomes is reduced by half, resulting in haploid gametes.
Why is chromosome reduction important in meiosis?
Chromosome reduction is essential to maintain the species’ characteristic chromosome number from generation to generation. Without chromosome reduction, the chromosome number would double with each generation, leading to inviability.
What is independent assortment and how does it occur in meiosis?
Independent assortment refers to the random orientation of chromosomes during meiosis I, which results in the independent distribution of alleles to gametes. This process contributes to the genetic diversity observed in offspring.