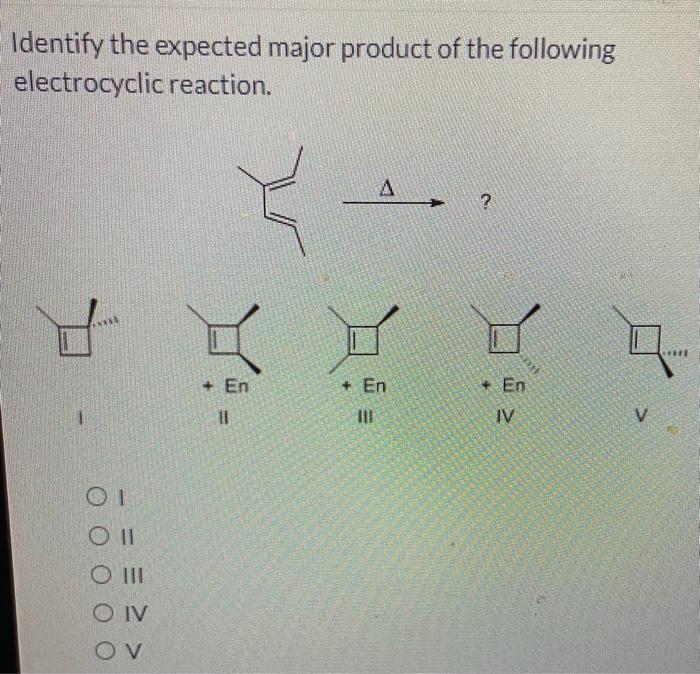
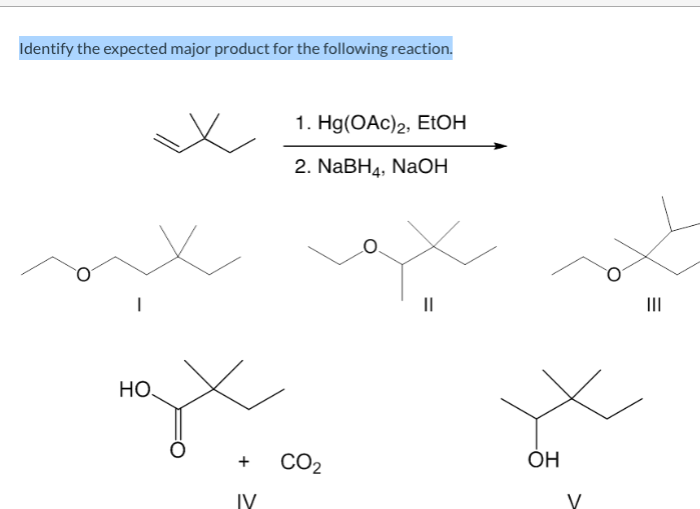
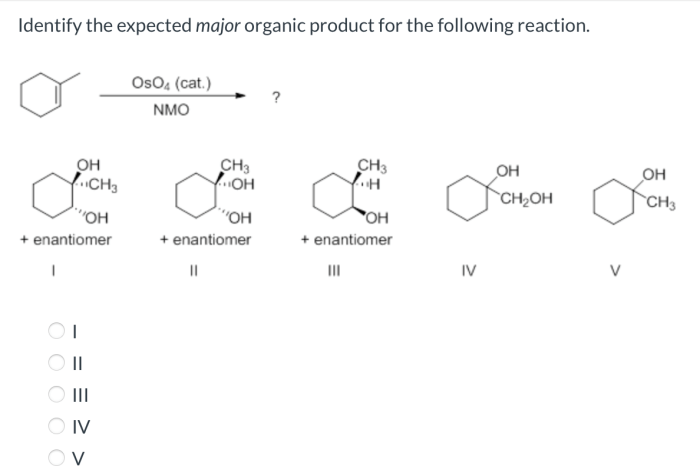
Identify the expected major product for the following reaction – In the realm of organic chemistry, the identification of the expected major product is a fundamental skill. This process requires an understanding of reaction mechanisms, regio- and stereoselectivity, and the factors that influence product formation. By mastering these concepts, chemists can predict the outcome of reactions and design synthetic strategies accordingly.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of identifying the expected major product, providing a detailed framework for understanding and applying these principles.
Identifying the Major Product of Organic Reactions: Identify The Expected Major Product For The Following Reaction
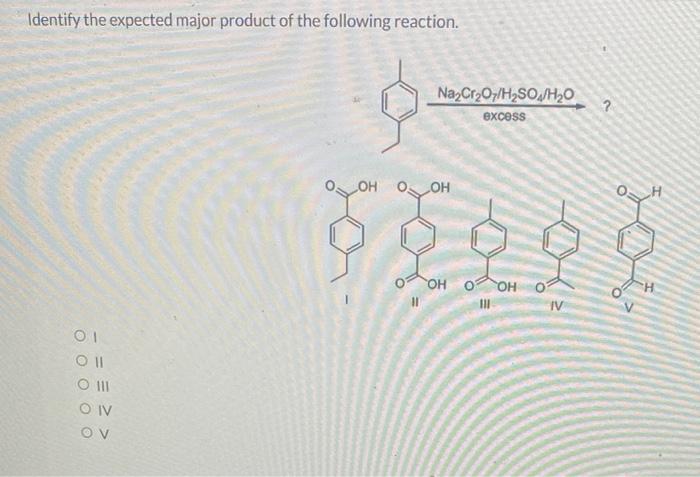
Organic reactions involve the transformation of one set of molecules (reactants) into another set of molecules (products). In many cases, a reaction can produce multiple products, and it is important to be able to identify the major product, which is the product that forms in the greatest quantity.
Identify the Reactants and Products, Identify the expected major product for the following reaction
The first step in identifying the major product is to identify the reactants and products involved in the reaction. The reactants are the starting materials, and the products are the substances that are formed. The reaction equation is a chemical equation that shows the reactants on the left-hand side and the products on the right-hand side.
Determine the Major Product
The major product is the product that is formed in the greatest quantity. There are a number of factors that can influence the formation of the major product, including the reaction mechanism, the regioselectivity, and the stereoselectivity.
Analyze the Reaction Mechanism
The reaction mechanism is the step-by-step process by which the reactants are converted into products. The reaction mechanism can be used to identify the intermediate species and transition states that are involved in the reaction.
Evaluate the Regio- and Stereoselectivity
The regioselectivity of a reaction refers to the preference for one regioisomer over another. The stereoselectivity of a reaction refers to the preference for one stereoisomer over another. The regioselectivity and stereoselectivity of a reaction can be used to identify the major product.
Provide Examples
The following are some examples of reactions where the expected major product can be identified:* The addition of hydrogen cyanide to an aldehyde or ketone produces a cyanohydrin. The major product is the cyanohydrin that is formed by the addition of hydrogen cyanide to the carbonyl carbon.
- The Diels-Alder reaction is a cycloaddition reaction that produces a cyclohexene. The major product is the cyclohexene that is formed by the addition of the diene to the dienophile.
- The Friedel-Crafts reaction is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction that produces an alkylbenzene. The major product is the alkylbenzene that is formed by the addition of the alkyl group to the aromatic ring.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the key factors that influence the formation of the major product in organic reactions?
The formation of the major product is influenced by factors such as the stability of the transition state, the reactivity of the reactants, and the reaction conditions.
How can regio- and stereoselectivity affect the identity of the major product?
Regioselectivity determines the position of the functional group in the product, while stereoselectivity determines the spatial arrangement of the atoms in the product. Both regio- and stereoselectivity can have a significant impact on the identity of the major product.
What are some common methods for identifying the expected major product in organic reactions?
Common methods include analyzing the reaction mechanism, considering the stability of the intermediates, and using computational chemistry tools.