Art-labeling activity white blood cells sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The art of labeling white blood cells, a cornerstone in hematological analysis, plays a pivotal role in unraveling the complexities of these vital immune cells.
Through this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the diverse techniques employed in art-labeling, examining their advantages and limitations. Moreover, we uncover the invaluable applications of art-labeling in diagnosing and monitoring hematological disorders, highlighting its ability to differentiate between normal and abnormal white blood cells.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
1. Introduction
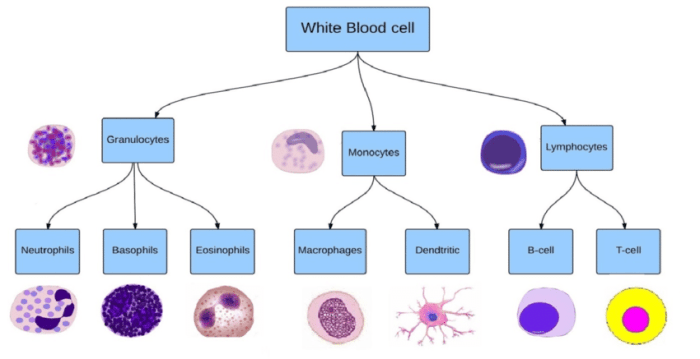
Art-labeling activity refers to the application of specific dyes or stains to white blood cells (WBCs) to enhance their visibility and enable their identification and classification under a microscope. This technique plays a crucial role in the analysis of WBCs, providing valuable insights into their morphology, cellular components, and functional characteristics.
Art-labeling techniques are essential for accurate diagnosis and monitoring of hematological disorders, as they allow for the differentiation between normal and abnormal WBCs. These techniques aid in the identification of specific cell types, the detection of abnormal cell morphology, and the assessment of WBC function.
2. Types of Art-Labeling Techniques
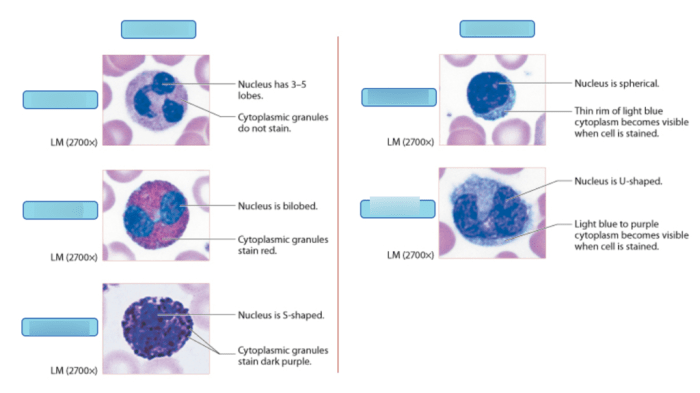
Various art-labeling techniques are employed for WBC analysis, each with its advantages and limitations. The most commonly used techniques include:
- Romanowsky staining: This method utilizes a combination of acidic and basic dyes to differentiate WBCs based on their nuclear and cytoplasmic characteristics.
- Wright-Giemsa staining: A modification of Romanowsky staining, Wright-Giemsa provides improved visualization of cell morphology and cytoplasmic granules.
- May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining: Similar to Wright-Giemsa staining, this technique offers enhanced visualization of nuclear and cytoplasmic details.
- Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining: This technique specifically stains carbohydrates and glycoproteins, highlighting structures such as glycogen and mucin.
- Sudan black B staining: Used to identify lipid-containing cells, such as monocytes and macrophages.
- Immunocytochemistry: This technique employs antibodies specific to particular antigens to label and identify specific WBC subpopulations.
The choice of art-labeling technique depends on the specific diagnostic or research objectives, as each technique offers unique advantages and limitations.
3. Applications of Art-Labeling in White Blood Cell Analysis
Art-labeling techniques have wide-ranging applications in the analysis of WBCs, including:
- Differential WBC count: Art-labeling enables the identification and quantification of different WBC types, including neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils.
- Identification of abnormal WBCs: Art-labeling helps detect abnormal WBC morphology, such as immature or atypical cells, which can indicate hematological disorders.
- Assessment of WBC function: Certain art-labeling techniques, such as immunocytochemistry, can assess the functional capabilities of WBCs, such as phagocytosis and antibody production.
- Diagnosis of hematological disorders: Art-labeling plays a crucial role in diagnosing conditions such as leukemia, lymphoma, and infectious diseases.
- Monitoring treatment response: Art-labeling can be used to monitor the response of WBCs to treatment, such as chemotherapy or immunosuppressive therapy.
4. Recent Advances in Art-Labeling Techniques
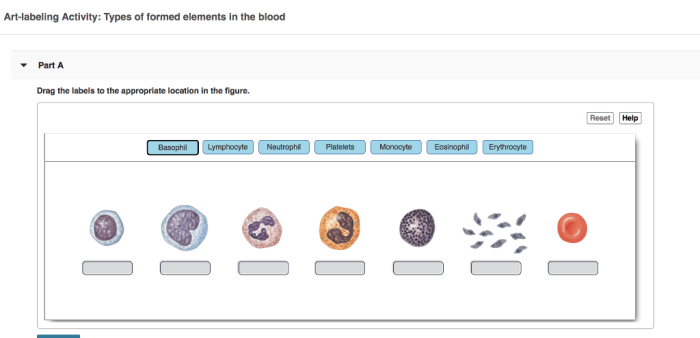
Advancements in art-labeling techniques have significantly improved the specificity, sensitivity, and efficiency of WBC analysis:
- Automated staining systems: These systems provide consistent and standardized staining, reducing inter-observer variability and improving accuracy.
- Multiplex immunofluorescence staining: This technique allows for simultaneous labeling of multiple antigens, enabling comprehensive analysis of WBC subpopulations.
- Flow cytometry: This technique combines art-labeling with cell sorting, allowing for rapid and accurate quantification of specific WBC populations.
- Digital image analysis: Automated image analysis systems provide objective and quantitative assessment of WBC morphology and cellular characteristics.
These advancements have enhanced the clinical utility of art-labeling in WBC analysis, leading to more precise diagnosis and improved patient management.
5. Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the advancements, art-labeling techniques face challenges and offer opportunities for future research:
- Inter-observer variability: Subjective interpretation of stained WBCs can lead to variability in results.
- Limited sensitivity: Certain art-labeling techniques may not be sensitive enough to detect subtle changes in WBC morphology.
- Cost and time constraints: Manual art-labeling methods can be time-consuming and expensive.
Future research directions include the development of standardized staining protocols, improved image analysis algorithms, and the exploration of novel art-labeling targets to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of WBC analysis.
Essential Questionnaire: Art-labeling Activity White Blood Cells
What is art-labeling activity?
Art-labeling activity refers to a range of techniques used to label white blood cells with specific dyes or antibodies, allowing for their identification and classification under a microscope.
How does art-labeling aid in white blood cell analysis?
Art-labeling enables the visualization and differentiation of various white blood cell types based on their morphology, size, and the presence of specific surface markers, facilitating accurate diagnosis and monitoring of hematological disorders.
What are the different types of art-labeling techniques?
Common art-labeling techniques include Wright-Giemsa staining, May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining, and immunophenotyping using flow cytometry, each with its own advantages and limitations.